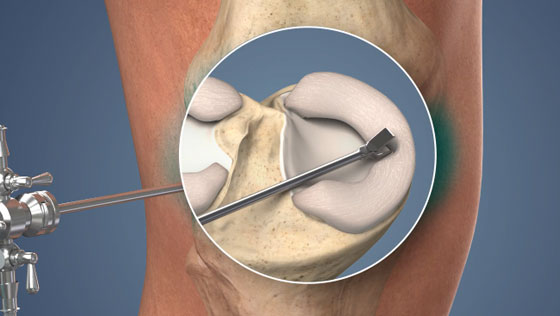
What is Torn Meniscus Repair?
Torn meniscus repair is a surgical procedure that is typically performed arthroscopically in order to repair torn cartilage inside the knee joint.
Key statistics about Torn Meniscus Repair
- Most meniscal repairs are performed on patients younger than 40 years old[1]
- Approximately 85% of traumatic meniscal tears are accompanied by ACL tears[1]
- Meniscus repairs that are performed within 6 weeks of injury have a success rate of 83%, while later repairs report a success rate of only 52%[2]
Expert Insights
When should you have a Meniscal Tear repaired? - Daniel Cooper, MD
Knee Anatomy
The knee joint is formed by three bones: the femur (thigh bone), the tibia (shin bone), and the patella (kneecap).
The menisci are two crescent-shaped pieces of cartilage positioned on either side of the knee, between the tibia and femur. The medial meniscus and lateral meniscus absorb shock, disperse weight, and reduce friction as the knee moves.

What are Meniscus Tears?
Meniscus tears are some of the most commonly-occurring knee injuries. There are two primary categories of meniscus tears:
- Traumatic tears: acute tears that are the result of traumatic injury typically involving pivoting or twisting of the knee, and commonly occur in athletes
- Degenerative tears: chronic tears that are often a normal consequence of aging and commonly occur in older individuals
Meniscal tears occur in a variety of patterns such as: radial tears, flap tears, transverse tears, longitudinal tears, bucket-handle tears, and horn tears.
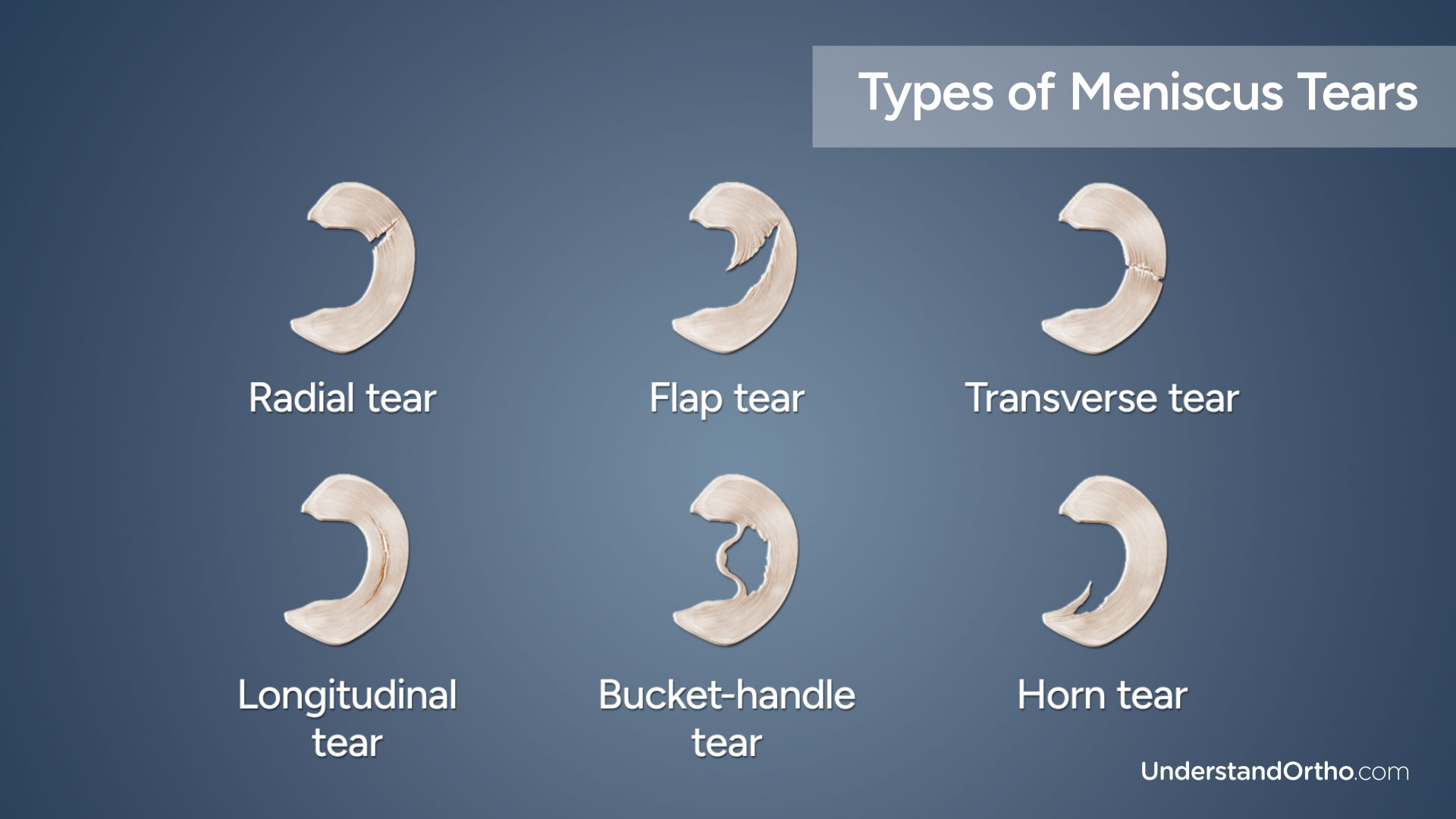
Meniscal tears can cause pain, swelling, instability, and reduce the range of motion of the knee. Left untreated, meniscal tears can worsen and eventually lead to osteoarthritis in the affected knee.
Why is Torn Meniscus Repair performed?
There are a variety of techniques used to address meniscus tears including nonsurgical options, meniscus repair, meniscus trimming, and meniscus removal and transplant. The age of the patient and the location and type of tear will determine which technique will be used to address the injury.
Meniscus repair is typically performed to address traumatic meniscal tears in younger, active individuals. Longitudinal tears that occur in an area with an adequate blood supply for healing are most likely to result in meniscus repair.
How is Torn Meniscus Repair performed?
- The surgeon will make small incisions around the knee joint and an arthroscope will be inserted into one of the incisions.
- Saline solution is pumped into the joint to expand it and improve visualization.
- Images from the arthroscope are sent to a video monitor where the surgeon can see inside the joint.
- The torn edges of the meniscus are reattached, typically using sutures, anchors, resorbable tacks, or barbed fixation devices, depending upon the specific injury.
- ACL tears can occur at the same time as meniscus tears and ACL reconstruction may occur during the same surgery as meniscus repair.
- Finally, the saline solution is drained, instruments are removed, and the incisions are closed using sutures.
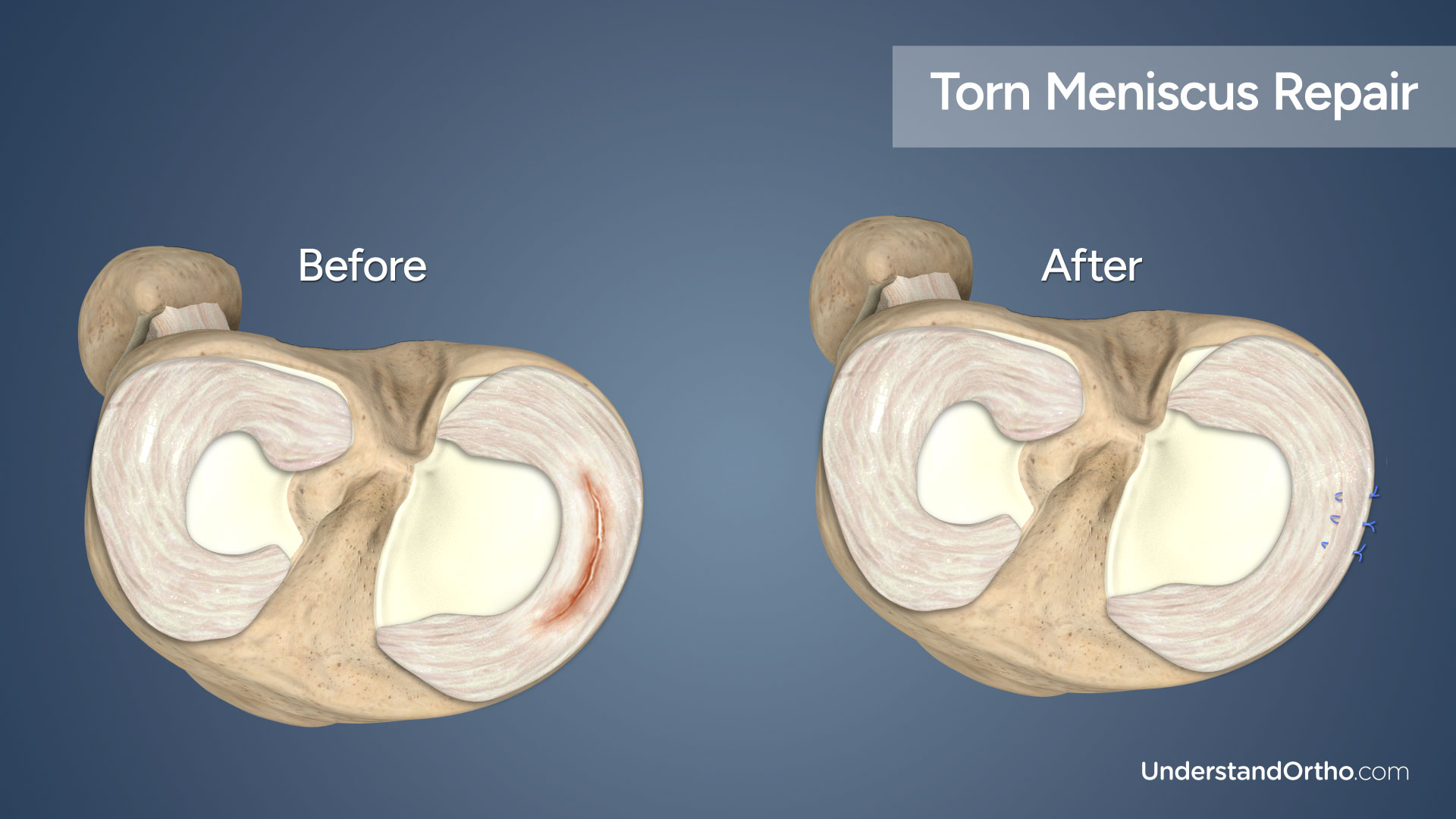
What are the risks of Torn Meniscus Repair?
It is uncommon to experience complications from meniscus repair, but potential risks may include:
- Infection
- Blood clots
- Nerve or blood vessel damage
- Knee stiffness
How long does it take to recover from Torn Meniscus Repair?
-
24 hours after surgery
Physical therapy will begin and pain killers will be prescribed. -
1-3 days after surgery
Most patients are discharged from the hospital and will be able to walk with crutches. -
2 weeks after surgery
Any non-dissolvable sutures are removed and bruising and swelling begin to subside. -
4-6 weeks after surgery
Most patients are able to walk without crutches and resume driving and most daily activity. -
3-6 months after surgery
Most patients are fully recovered from meniscus repair.
What are the results of Torn Meniscus Repair?
The objective of torn meniscus repair is to preserve healthy meniscus tissue in order to prevent osteoarthritis, restore knee function, and reduce pain. Meniscus repair is an effective procedure to repair knee cartilage damage, and most patients are able to return to their pre-injury abilities.
Find an Orthopedic Doctor in Your Area